Universitas 'Aisyiyah Yogyakarta
Green Campus- Energy Efficient Appliances Usage
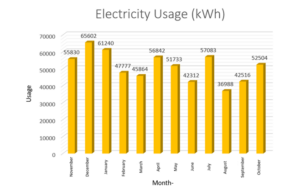
- Electricity Usage per Year (in Kilowatt hour)
- Elements of Green Building Implementation as Reflected in All Construction and Renovation Policies
- Greenhouse gas emission reduction program
- Number of innovative program(s) during Covid-19 pandemic
- Impactful university program(s) on climate change
UNISA Yogyakarta has installed LED lights in almost all areas to save energy since the building’s construction. Some areas such as Building C Block 1 UNISA and Rusunawa Building. Buildings A use almost 75% of the LED lights and Building B uses 25% of the LED lights, particularly in the classrooms and the staff room. Meanwhile, other efficient technology applications are still in the planning process, such as electrical and water devices. Inline, to support energy savings, UNISA Yogyakarta invites all civitas to turn off the lights after use and use stairs to decrease the lift occupancies.
- Figure 1. Some types of LED lights in various UNISA Yogyakarta buildings
- Figure 2. Invitation to save energy
- Figure 3. Energy Saving Activities with no elevator
In total, UNISA Yogyakarta consumed the electrical energy during 12 months from July 2020 to July 2021 is about 616291 kWh. The building occupies electrical energy for lighting, cooling, fans, elevators, CCTV, and water pumps. The use of electrical energy at UNISA Yogyakarta uses seven PLN Customer IDs for the entire UNISA Yogyakarta campus building. Many buildings have decreased electricity usage in line with the decreasing number of visitors during pandemic covid-19. Consequently, the building activities and electrical consumption during the Covid-19 Pandemic also decreased.
Almost all the main buildings of the UNISA Yogyakarta Campus have implemented elements of the green buildings concept. UNISA Yogyakarta campus strongly supports the use of natural lighting systems and natural ventilation systems. For example, Buildings A, B, C, Rusunawa, and Campus 1 have the maximum use of glass to cover the entire building envelope. So that lighting can meet the needs of activities in all spaces in the building, particularly during working hours. In addition, the ventilation and window openings in the exterior and interior areas of the building utilize living glass. Flexible openings glass (opened-closed) help people who stay in the room have an option to turn on the air conditioning or open the windows to access the air. In addition, active windows also help people get fresh air for the needs of the building. The building is equipped with shading to keep the building from being glared at, and the sun’s heat does not flood into the space, like double facades on the exterior with anti-sun radiation glass. The use of vegetation as natural sun shading and the use of window blinds support adaptive thermal comfort.
- Figure 1. Double Facade to screen glare and heat from the sun that enters the room of Building A
- Figure 2. Natural light for saving energy
- Figure 3. Vegetation as natural sun shading with window openings
- Figure 4. The use of living glass as a natural ventilation system in all areas of Buildings A, B, C, Rusunawa and Campus 1
- Figure 5. Use of Window blinds as part of Adaptive Thermal Comfort
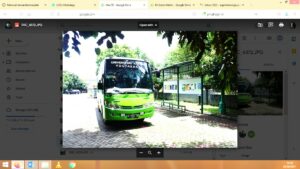
UNISA Yogyakarta is under development to achieve all aspects supporting the Sustainability Goals, particularly in physical facilities to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. To begin with, UNISA Yogyakarta collaborated with public transportation to provide a bus station in front of the campus at Ringroad. This collaboration also resulted in the new route that passed through the UNISA Yogyakarta campus. So, the academic community can afford the public bus to come to UNISA Yogyakarta. This collaboration aims to reduce private vehicles occupancy, which results in increased gas emissions. In addition, UNISA Yogyakarta facilitated the movement between campus one and campus block A Unisa Yogyakarta at ring road using the UNISA private shuttle bus. This policy supports the reduction of public transportation for mobility between two different campus locations.
- Figure 1. Shuttle Bus and Trans Jogja Bus Stop in front of UNISA Yogyakarta Campus on the Ringroad
- Figure 2. UNISA Yogyakarta Private Shuttle Bus for inter-campus transportation
The Covid-19 pandemic has an impact on innovating so that all sectors can continue to run according to their functions. UNISA Yogyakarta designed several innovation programs to maintain sustainability but still pay attention to the health and safety of the community. Some of these innovation programs include:
- Manufacture of hand sanitizer products
To overcome the scarcity of hand sanitizers that occurred in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, the University of ‘Aisyiyah Yogyakarta produced hand sanitizers independently through the Biotechnology study program. The hand sanitizer ingredient from the Biotechnology study program contains lavender extract, which can help prevent mosquito bites because dengue transmission is another threat than the transmission of the Covid-19 virus. - Islamic Boarding School
As a health-minded campus with Islamic values, Universitas ‘Aisyiyah Yogyakarta takes a holistic approach for COVID-19 sufferers who live in the Unisa shelter through the Covid-19 Islamic boarding school program. More than 500 COVID-19 patients have been treated at the UNISA Yogyakarta COVID-19 Islamic boarding school. - Hybrid learning
The President of UNISA Yogyakarta implemented policies related to hybrid learning to achieve learning objectives while prioritizing the safety and health of the community. The policy also supports training activities and strengthening infrastructure during the COVID-19 pandemic. - Swa Room Visit
The Unisa Yogyakarta Covid-19 Task Force innovated by creating the “SwaKunjungan Ruang” application as a digital tracing effort that makes it easier to track if a Covid-19 case is found at UNISA Yogyakarta.
- Figure 1. Innovation in producing hand sanitizers to overcome the scarcity of hand sanitizers during the pandemic
- Figure 2. Innovation in producing hand sanitizers to overcome the scarcity of hand sanitizers during the pandemic
- Figure 3. The “COVID-19 Islamic Boarding School” program for COVID-19 sufferers at Rusunawa UNISA Yogyakarta
- Figure 4. The “COVID-19 Islamic Boarding School” program for COVID-19 sufferers at Rusunawa UNISA Yogyakarta
- Figure 5. The “COVID-19 Islamic Boarding School” program for COVID-19 sufferers at Rusunawa UNISA Yogyakarta
- Figure 6. Offline lecture activities by implementing strict health protocols
To achieve a green campus in terms of Climate Change, UNISA Yogyakarta has some agenda. For example, programs carried out by the Faculty of Science and Technology UNISA Yogyakarta, such as the general public education program by the Biotechnology Study Program to educate the public regarding the creation of sound waste that supports creating a healthy environment. In addition, UNISA Yogyakarta Architecture also organizes several activities motivated by Climate Change, such as the Implementation of Green Buildings in Indonesia. The educational program is intended for the public and is free of charge. In addition, the Biotechnology Study Program also innovates to produce Bio-Straw, namely the use of natural materials to create environmentally friendly straws to reduce plastic waste, which indirectly causes climate change.
- Figure 1. Good Waste Education Training Program for Creating a Good Environment held for the public nationally
- Figure 2. Public Education Program on the Implementation of Green Building in Indonesia
- Figure 3.Bio-straw innovations that have been sold and published to the general public